Introduction
Deployments can make or break a release.
You’ve probably experienced that nervous moment when you hit “Deploy” — fingers crossed, hoping nothing breaks in production. The truth is, deployment failures happen to even the best teams. But there’s a smarter way to minimize risk and build confidence in every release – through DevOps automation
Why Deployment Failures Happen
Before we fix the problem, let’s understand why it happens in the first place.
Most deployment failures are caused by:
- Manual configuration mistakes
- Inconsistent environments between dev, test, and prod
- Missing dependencies or version mismatches
- Incomplete rollbacks after a failed release
- Lack of visibility or monitoring during deployment
When teams rely heavily on manual steps, it’s only a matter of time before something slips through the cracks.
How DevOps Automation Changes the Game
DevOps automation makes your deployment process predictable, consistent, and testable — no more “it worked on my machine” nightmares.
Here’s how it helps:
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC):
Tools like Terraform or ARM templates ensure your environments are always consistent — no manual setup surprises. - Continuous Integration (CI):
Every code change gets automatically built and tested. You catch issues early before they ever reach production. - Continuous Deployment (CD):
Automated pipelines handle the release process, ensuring smooth rollouts every time. - Automated Rollbacks:
If something goes wrong, the system automatically reverts to the last known good version — saving you from long downtimes. - Configuration Management:
Tools like Ansible or Chef make sure every server and container is configured the same way, every time.
Automation replaces guesswork with reliable, repeatable processes.
Scaling Automation Across Teams and Environments
As your organization grows, so does the complexity of deployments.
Here’s how to keep things running smoothly at scale:
- Use standardized CI/CD templates across teams.
- Store all infrastructure and pipeline definitions in Git.
- Adopt containerization with Docker and orchestration with Kubernetes for consistent environments.
- Set up automated tests and quality gates before every deployment.
- Implement canary or blue-green deployments to release gradually and safely.
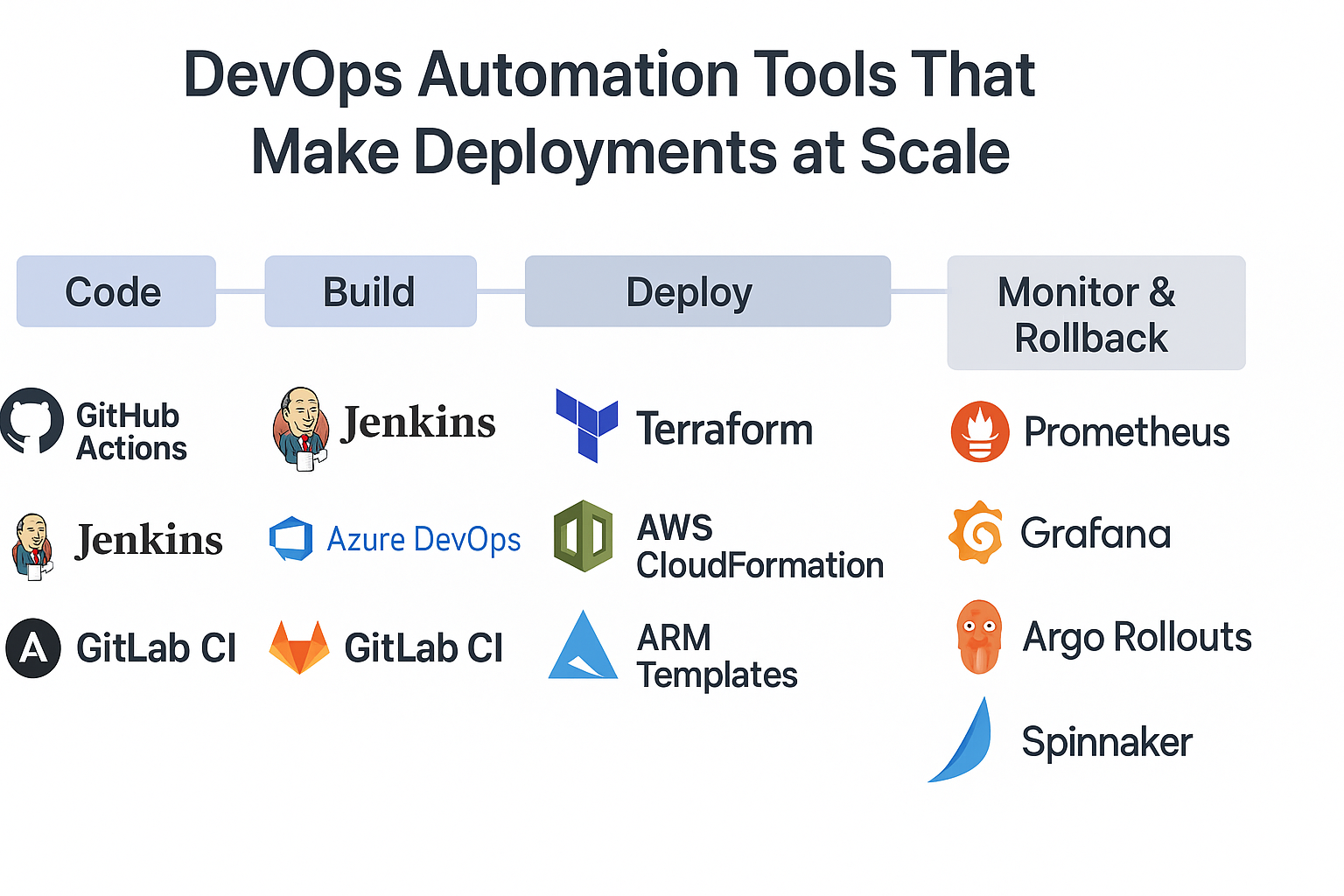
Tools That Make It Easier
Real-World Example: Netflix’s Deployment Automation
Think about Netflix — millions of users streaming at the same time. They can’t afford downtime or buggy updates. So, how do they deploy new code almost every day without breaking anything?
They rely on DevOps automation to handle everything smoothly.
1. Code Stage
Developers push code to GitHub (or GitLab).
As soon as they do that, an automated trigger kicks in — no one manually clicks “Build.”
2. Build Stage
Tools like Jenkins or GitHub Actions automatically test the code, build Docker images, and verify if everything works fine.
If something fails here, the system sends an alert — preventing bad code from moving forward.
3. Deploy Stage
Once tests pass, tools like Spinnaker or Terraform deploy the application automatically to servers (like AWS, Azure, or Kubernetes).
It’s done in small batches — this is called canary deployment — so only a few users get the new version first.
4. Monitor & Rollback
Tools like Prometheus and Grafana constantly watch the system.
If something unusual happens (say, errors increase), the system automatically rolls back to the previous version — no human intervention needed.
Best Practices to Keep in Mind
- Automate everything that’s repeatable.
- Keep pipelines and scripts version-controlled.
- Always include testing in your pipeline.
- Monitor deployments in real-time.
- Use gradual rollout strategies like canary or blue-green.
Remember: automation doesn’t eliminate problems — it helps catch them early and recover faster.
Conclusion
At the end of the day, DevOps automation isn’t just about speed — it’s about stability and trust.
When your team can deploy confidently and consistently, innovation flows faster, and customers get a smoother experience.
So, if you’re still manually deploying code, it’s time to level up.
Start small, automate your most common steps, and watch your deployment failures disappear over tim
